Chemical bonding refers to the formation of bonds by the forces that hold atoms together to make molecules or compounds.
Chemical bonds include ionic (complete transfer to valence electrons between atoms), covalent (sharing of electrons between pairs of atoms) and metallic (refers to bonds between conduction electrons due to electrostatic forces) bonds.
Let’s discuss some questions regarding this topic without further introductions.
Chemical bonding questions
Question 1:
How many electrons are being shared between the two carbon atoms in Ethyne? The compound Ethyne has the lewis structure H−C≡C−H.
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 6
Answer 1:
6 electrons are being shared between the two carbon atoms in Ethyne. This is because three lines in the carbon atoms (in the Lewis structure) show three covalent bonds.
Since each covalent bond is a shared pair of the atom, there are six electrons being shared.
Question 2:
Ethane (C2H6) and ammonia (NH3) are covalent compounds and their dot and cross structure is shown below.
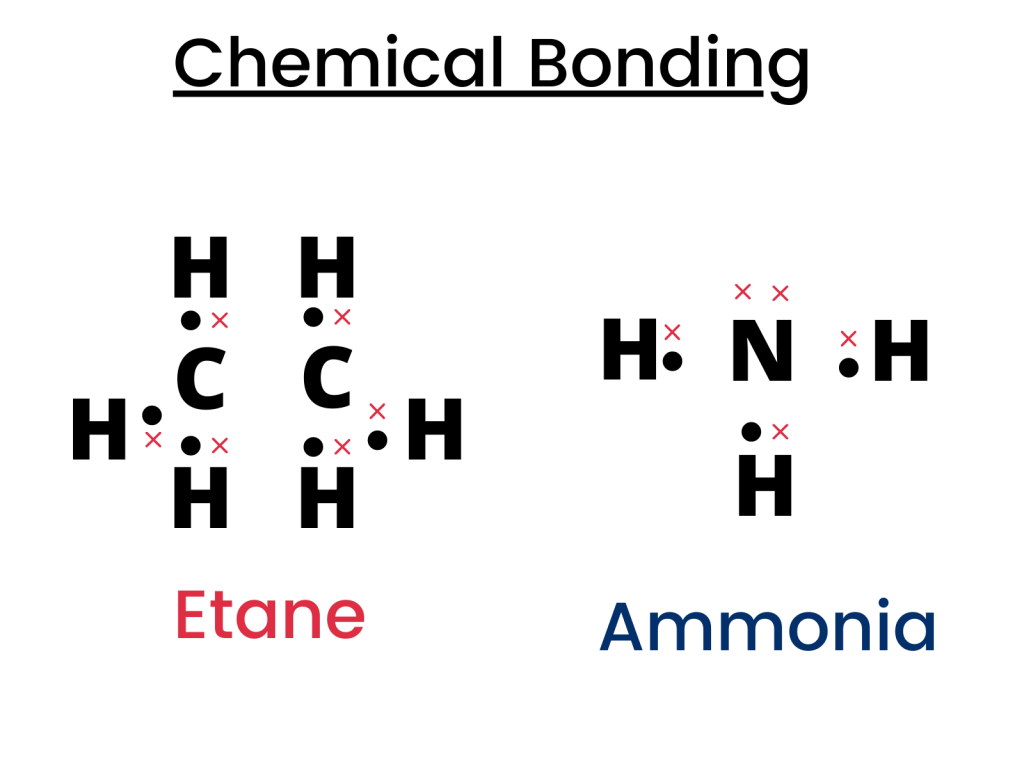
Which of the below-mentioned statements are correct?
- Unreacted nitrogen has four outer electrons
- A molecule of ethane contains twice as many hydrogen atoms as a molecule of ammonia
- In ethane, the covalent bond between the carbon atoms is formed by sharing two electrons, one from each carbon atom
Answer 2:
All of the three statements are correct because unreacted nitrogen has four outer (valence) electrons.
Moreover, there are six hydrogen atoms in a molecule of ethane while there are only three hydrogen atoms in the molecule of ammonia. Therefore, ammonia has half the number of hydrogen atoms as compared to ethane.
From the diagram, it is clearly visible that carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms share two electrons (one from Carbon and the other from Hydrogen).
Question 3:
The melting point of magnesium chloride is greater than that of sodium chloride. Explain, in terms of bonding, why is that so?
Answer 3:
Magnesium chloride contains Mg2+ and O2- ions while sodium chloride contains Na+ and Cl– ions.
The electrostatic forces of attraction between the ions in magnesium chloride are greater than the ions in sodium chloride due to larger positive and negative charge ions.
Therefore, greater energy is required to overcome the strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the ions in magnesium chloride while lesser energy is required for sodium chloride as compared to magnesium chloride.
Therefore, the melting point of magnesium chloride is greater.
Question 4:
Which of the following electron arrangement is that of a metallic element?
- 2, 1 (A)
- 2, 4 (B)
- 2, 5 (C)
- 2, 7 (D)
Answer 4:
A is the correct answer that says (2,1) is the electron arrangement of a metallic element.
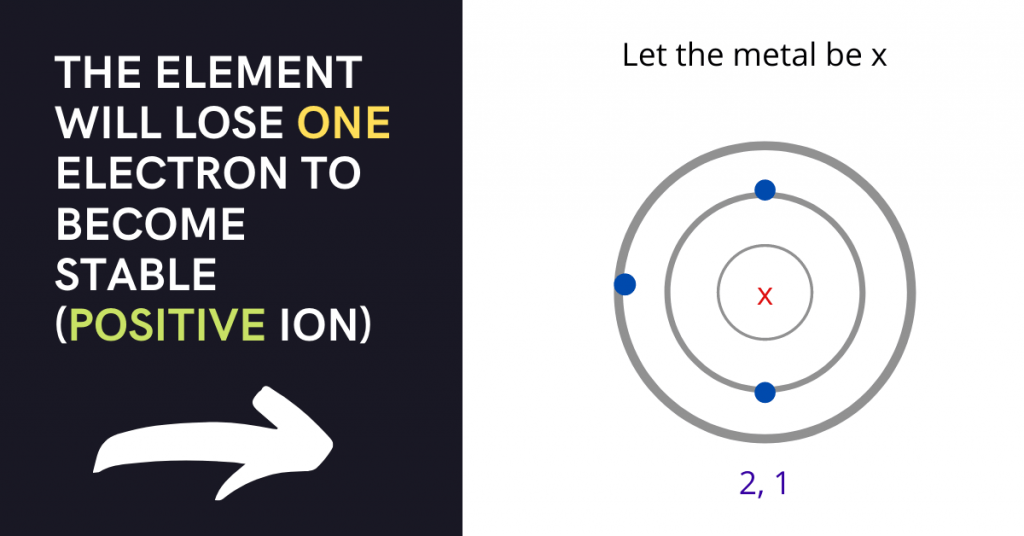
How is this the correct answer? Let me explain.
Metals have a greater tendency to lose electrons while non-metals have a greater tendency to gain electrons. The configuration (2, 1) means that the element will lose one electron to become stable.
The arrangement (2, 4) means that the element will gain four electrons to become stable while the arrangement (2, 5) says that the element will gain three electrons to become stable.
The arrangement (2, 7) means that the element will gain one electron to become stable. As a result, A is the correct answer because it is the only case in which an electron is lost.
Question 5:
Element X has the electronic structure of 2, 8, 8, 1 while element Y has the electronic structure of 2, 8, 6. What type of bond is made when X and Y react and what is the formula of the compound?
Type of compound Formula
A. Covalent bond X2Y
B. Covalent bond XY2
C. Ionic bond X2Y
D. Ionic bond XY2
Answer 5:
C is the correct answer and let me help you get to the answer.
The electron arrangement 2, 8, 8, 1 means that the element will lose one electron to become stable (note that metals lose electrons to become ions).
Further reading:
Energy changes | GCE O Level Chemistry (5070)
However, electronic configuration 2, 8, 6 means that the element will gain two electrons to become stable (note that non-metals gain electrons to become negative ions).
An ionic compound is a compound that is formed between a metal and a non-metal while a covalent compound is formed between non-metals.
So from the above information, we can conclude that the bond formed is ionic because metal and non-metal react. How do we find out the formula of an ionic compound?
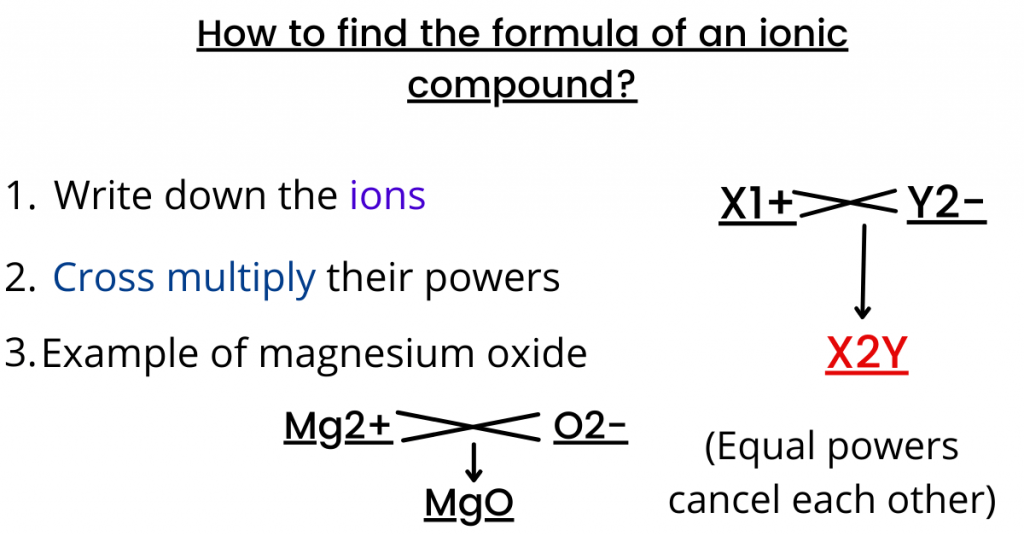
One method is to write down the ions of the compound first (in this case, X would have a +1 charge and Y would have a -2 charge).
Then, you cross multiply the charges to find out the formula of an ionic compound.
In simple words, first, you write the symbol and charge of a cation and then you write the symbol and charge of the anion. Finally, you combine the two ions into an electrically neutral compound.
Question 6:
What is the number of shared pairs of electrons in a molecule of ammonia?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
Answer 6:
There are three pairs of shared electrons in a molecule of ammonia (NH3) and therefore, A is the answer.
Look, nitrogen has five electrons in its valence shell and it requires three electrons to become stable. Where will it get those three electrons from?
As visible in the formula, there are three hydrogen atoms (NH3) and each hydrogen atom will give one electron to nitrogen. As a result, six electrons will be shared.
But, the question asks the number of pairs. Since six electrons are shared, there are three pairs. So, this information tells us that A is the correct answer.
Question 7:
Identify, which of the two statements given below is correct?
- In a “sea of electrons”, metals contain a lattice of negative ions
- The mobility of the electrons in the metals is the reason for their electrical conductivity
A. Statement one is correct but statement two is incorrect.
B. Both statements are correct and the second statement explains the first statement.
C. Both statements are correct but neither statement explains the other statement.
D. Statement one is incorrect while statement two is correct.
Answer 7:
D is the correct answer for this question.
Why is the first statement incorrect? The statement says that metals possess a lattice of negative ions which is incorrect because they contain a lattice of positive ions in the “sea of electrons”.
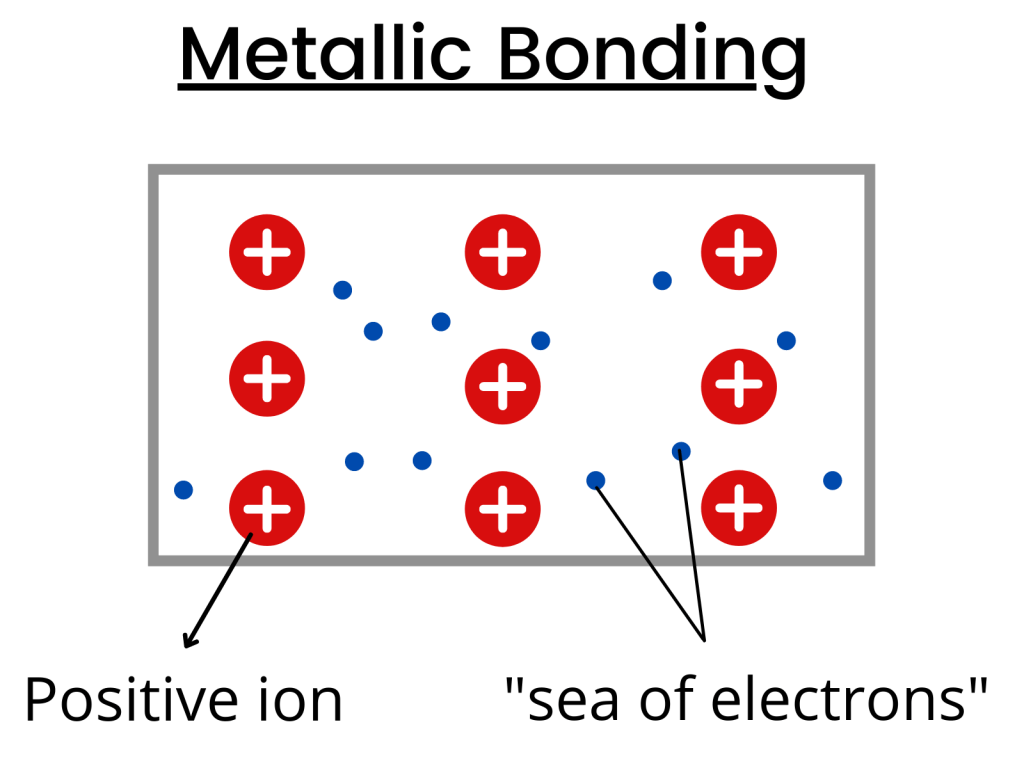
This is because metals lose electrons to become positively charged ions.
Moreover, the second statement is correct because the moving electrons help metals to conduct electricity.
In metal bonds, the electrons travel freely around the electron sea and since they are free to move towards any attraction, they help metals to conduct electricity.
Question 8:
Which one of the groups below only contains ionic compounds?
A. Copper (||) sulfate, methane, sodium chloride
B. Calcium oxide, magnesium oxide, sodium chloride
C. Calcium oxide, , magnesium oxide, hydrogen chloride
D. Carbon dioxide, hydrogen chloride, copper (||) sulfate
Answer 8:
The correct answer is B because it is the only group that contains all ionic compounds.
Recall that ionic compounds are formed between metals and non-metals (electrons are transferred) and only B is the group that fulfils this criterion. However, A contains methane (CH4) that has covalent bonds.
Similarly, there is covalent bonding in hydrogen chloride because electrons are shared while in ionic bonding, electrons are not shared but are transferred.
These are some chemical bonding questions. However, there are some important concepts in this topic which you should know as well. So, let’s discuss them.
Chemical bonding notes:
- Metals lose electrons to form positive ions (cations).
This is because when metals lose electrons, they attain the electronic configuration of a noble gas because noble gases are stable (they have complete valence electrons).
- Non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions (anions).
When non-metals gain electrons, they also attain the electronic configuration of noble gas and have a fully stable outer shell.
They have more valence electrons so they end up gaining electrons because it is easier for them to gain electrons than to lose electrons.
- Ionic compounds have ionic bonds and they have a giant lattice structure.
Ionic compounds conduct electricity in the molten or aqueous state. (In the molten or aqueous state, ionic compounds have free moving ions to conduct electricity).
Furthermore, ionic compounds have a very high melting and boiling point. They are soluble in water and insoluble in organic compounds.
- Covalent molecules can exist as simple molecular structure and giant molecular structure.
The simple molecular structure has weak intermolecular forces between the molecules. They have low melting and boiling point and they are not soluble in water.
The giant molecular structure has strong covalent bonds and they have a very high melting and boiling point and except for graphite, they do not conduct electricity.
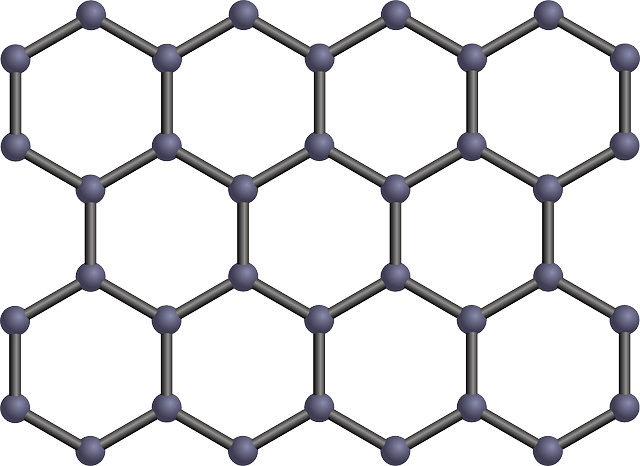
Note: Graphite conducts electricity because not all electrons are involved in bonding. The free-moving electrons allow it to conduct electricity.
- In metallic bonds, there are positive ions around the “sea of electrons”.
Apart, metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. They have high density, melting point and boiling point.
Finally, they are malleable (pressed into different shapes without breaking or cracking) and ductile (can be drawn into a thin wire).
These are some of the important concepts about the topic which you should know to solve the questions related to this topic.
Conclusion:
With this, our article about chemical bonding questions and notes has come to an end. I hope that all your questions have been answered and all queries have been cleared.
Ionic bonding, covalent bonding and metallic bonding are some of the topics discussed. Thank you very much for reading and staying with me till the end. Stay tuned for more.
